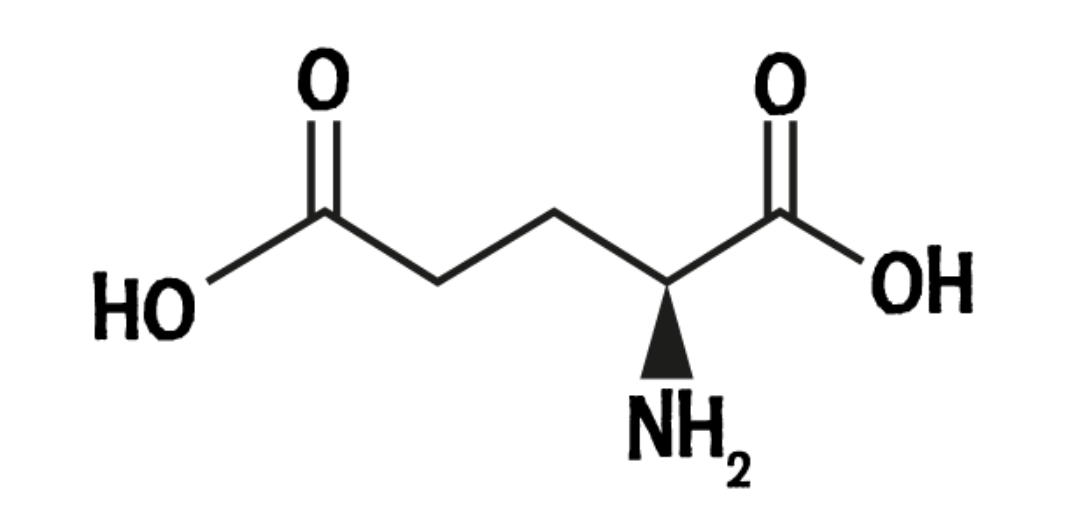
L-GLUTAMIC ACID
L-glutamic acid, also known as glutamate, is a non-essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in various biological processes within the body.
One of the most important functions of L-glutamic acid is its role as an excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, which is essential for brain function and cognitive processes such as learning and memory. L-glutamic acid plays a key role in energy production via the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle). This process helps convert carbohydrates, fats and proteins into energy that can be used by the body. Glutamic acid is also involved in the breakdown of proteins and the removal of ammonia.
Although it is not directly involved in the production of immune cells, L-glutamic acid plays an indirect role in supporting the immune system through its contribution to general cell health and function.
L-glutamic acid (as glutamate) is indeed a neurotransmitter in the brain and is essential for stimulating nerve cells and cognitive functions such as learning and memory.
Essential amino acid
Cannot be produced by the body and must be obtained through food or supplements
Non-Essential amino acid
Can be produced by the body itself in limited volumes









